12 Of The Best Forex Trading Strategies
The Different Types of Forex Trading Strategies
Forex traders use a range of trading tactics, strategies and techniques to decide the best entry and exit points – and timing – when buying or selling currencies. Market analysts and investors are always innovating and improving forex trading strategies, too. The aim is to devise the new methods that'll help them to better understand market movements. Here, FXCM explores some of the basic categories and major forex trading systems to which traders will often turn.
| Forex Strategy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Trend Trading |
|
|
| Range Trading |
|
|
| Momentum Trading |
|
|
| Swing Trading |
|
|
| Breakout Trading |
|
|
| Retracement |
|
|
| Reversal Trading |
|
|
| Position Trading |
|
|
| Carry Trade |
|
|
| Pivot Points |
|
|
| Day Trading |
|
|
| Forex Scalping |
|
|
Trend Trading
Trend trading is one of the most common forex trading strategies. . It's a strategy that involves spotting an upward or downward trend in a currency price movement. You'll then choose entry and exit points based on the position of the currency's price within the trend – and the trend's relative strength.
Traders often cite the phrase "the trend is your friend". This serves as a reminder that recent trends can be reliable indicators of where prices are likely to go and where to best set up your entry and exit points. Trend traders use various evaluation tools – such as moving averages, relative strength indicators, volume measurements, directional indices and stochastics.
Pros
Trend trading can be one of the best forex trading strategies for producing returns. Directional moves in price give active traders the chance to take on minimal risk. At the same time, they're able to pursue much larger rewards. The favourable risk vs reward scenarios improve capital efficiency. As such, it's possible to achieve solid profits with just a modest winning percentage.
Cons
Directional moves in forex pricing are often short-lived. There are myriad factors that can stop suddenly or even reverse a trend. Trending markets frequently move quickly, too, which makes it hard to secure good trade location. Unfortunately, many trend-following trades are ineffective as those who use this forex strategy miss out on the ideal entry.
As a result, they lose money by entering the market too late.
Example of Trend Trading
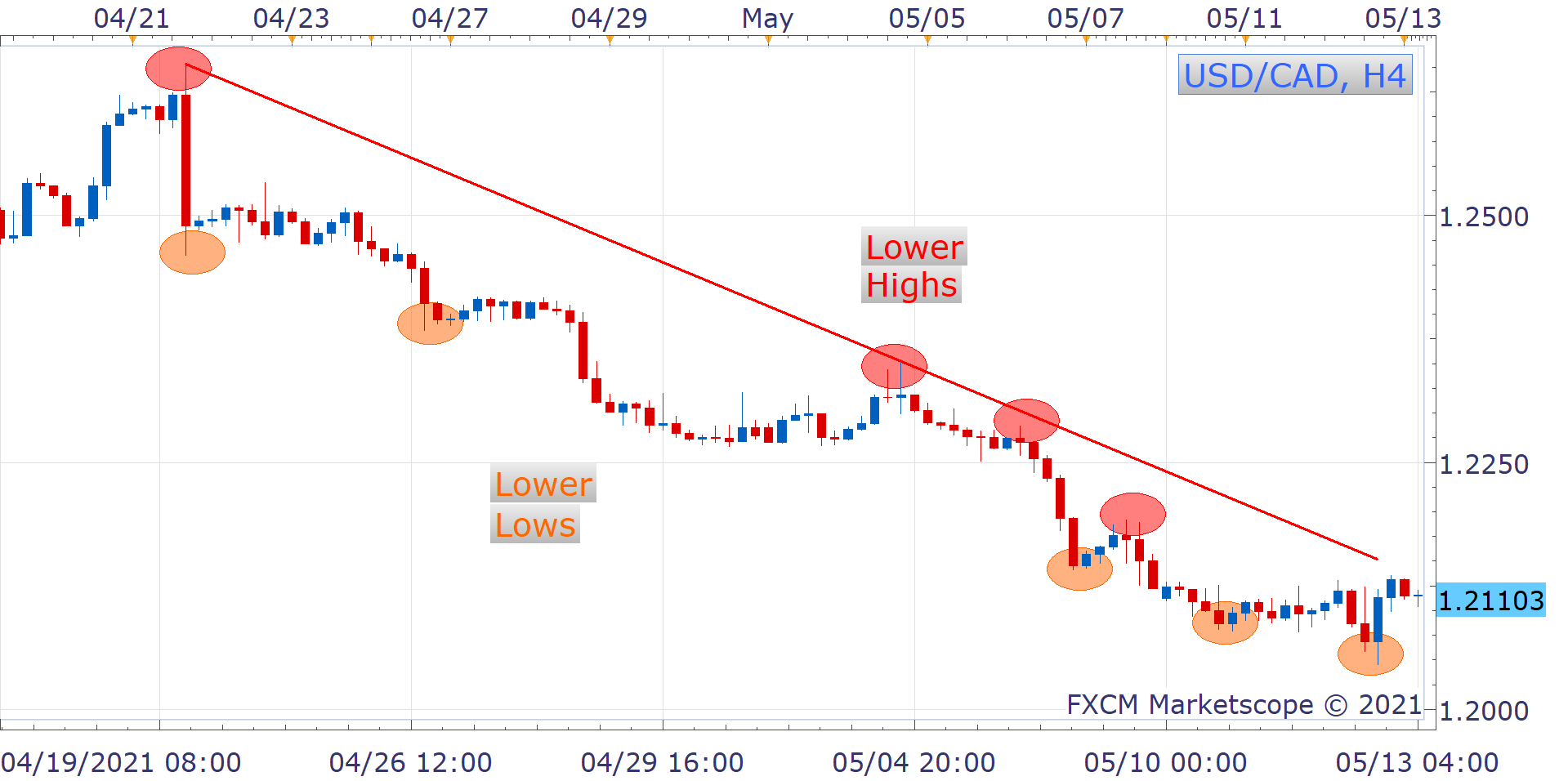
Range Trading
Want a simple, yet popular forex strategy? Range trading could be one of the best trading strategy to try. It's based on the idea that prices often stay within a steady and predictable range for a set period. That's particularly evident in markets involving stable and predictable economies – and currencies that aren't often subject to surprise news events.
As a forex trader, you can rely on the chance to frequently buy and sell at predictable highs and lows of resistance and support. You can sometimes do this repeatedly across one or more sessions. Range traders may use some of the same tools as trend traders to identify the ideal trade entry and exit levels. These tools include the relative strength index, the commodity channel index and stochastics.
Pros
As a forex trading strategy, this one requires less capital than many others to trade properly. Stop losses are typically aligned towards the extremes of any range, which makes each trade relatively affordable. Range bound markets are also common, so there's no shortage of potential opportunities. If an unexpected breakout develops, a sound forex strategy is wrong only once. That's because the market will establish a fresh trading range.
Cons
Consolidating markets typically move slowly because the limited participation leads to reduced price action. This means that bid/ask spreads may be wider. The cost of slippage to traders is also greater. Further, established ranges can be small – limiting the trade's profit potential.
A higher success rate is needed with this forex trading technique in order to sustain profitability and overcome drawbacks. That's due to the smaller profit targets, wider spreads and slippage.
Example of Range Trading
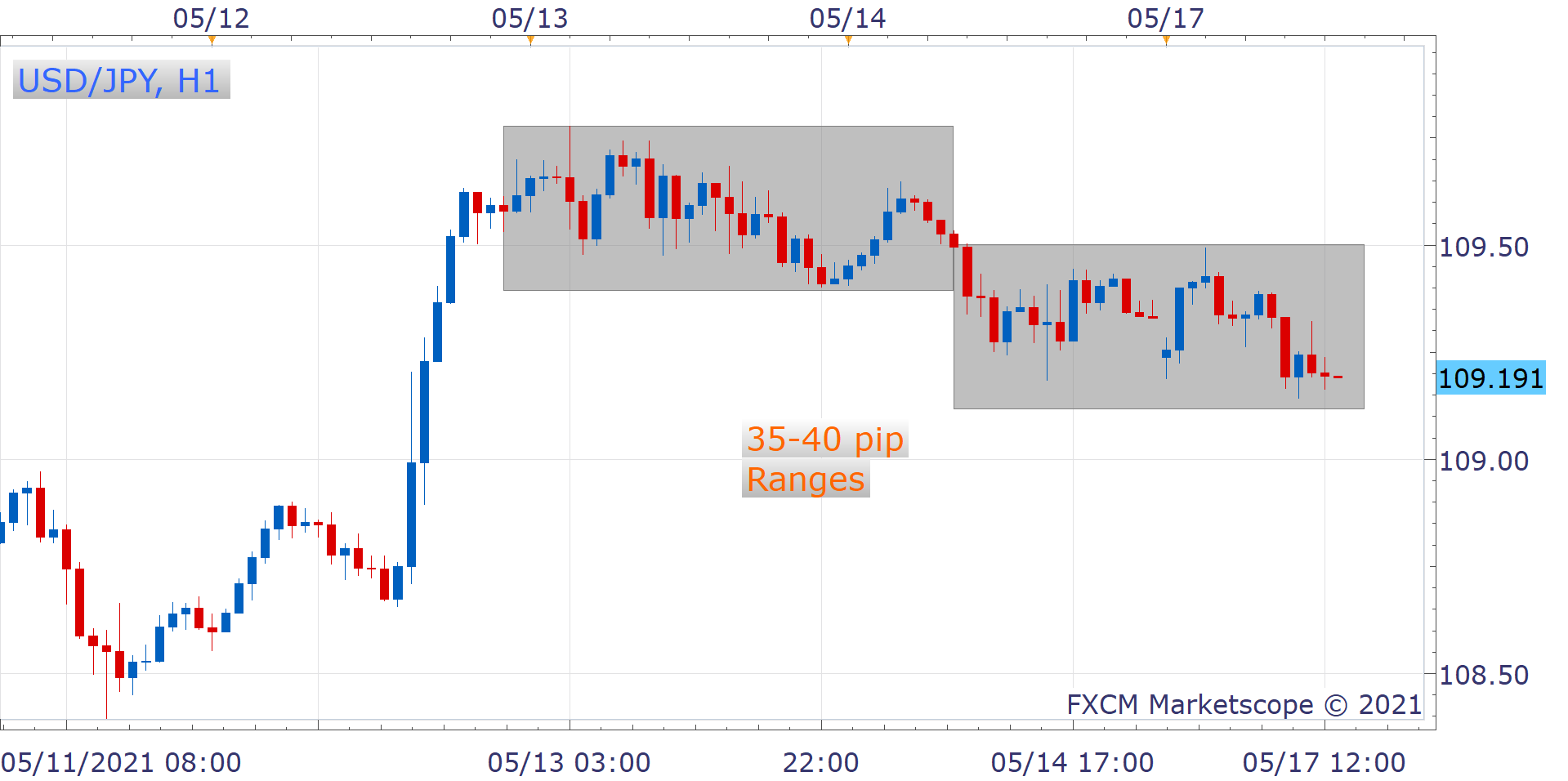
Momentum Trading
Momentum trading – and momentum indicators – are based on the notion that strong price movements in one direction or another are a likely sign that it'll continue in that direction.
In contrast, a weakening movement could show that a trend has lost strength. With that in mind, the price could be heading for a reversal. Momentum trading tactics may consider price and volume; often using analysis from graphic aides like oscillators and candlestick charts.
Pros
Implementing momentum forex trading strategies is relatively easy and affordable. Robust trends are obvious on any timeframe, which makes spotting setups routine. You can reduce your capital outlays because the success or failure of a specific trade is known quickly. This strategic functionality is ideal for cutting off losing trades, while letting winners run.
Cons
The momentum of price action can be fickle. It can often recede unexpectedly and it can be hard to accurately time the market as strong moves come on quickly. You need discipline to choose this forex strategy as there is a temptation to 'chase' a missed entry. But doing that could lead to unwarranted losses.
Example of Momentum Trading
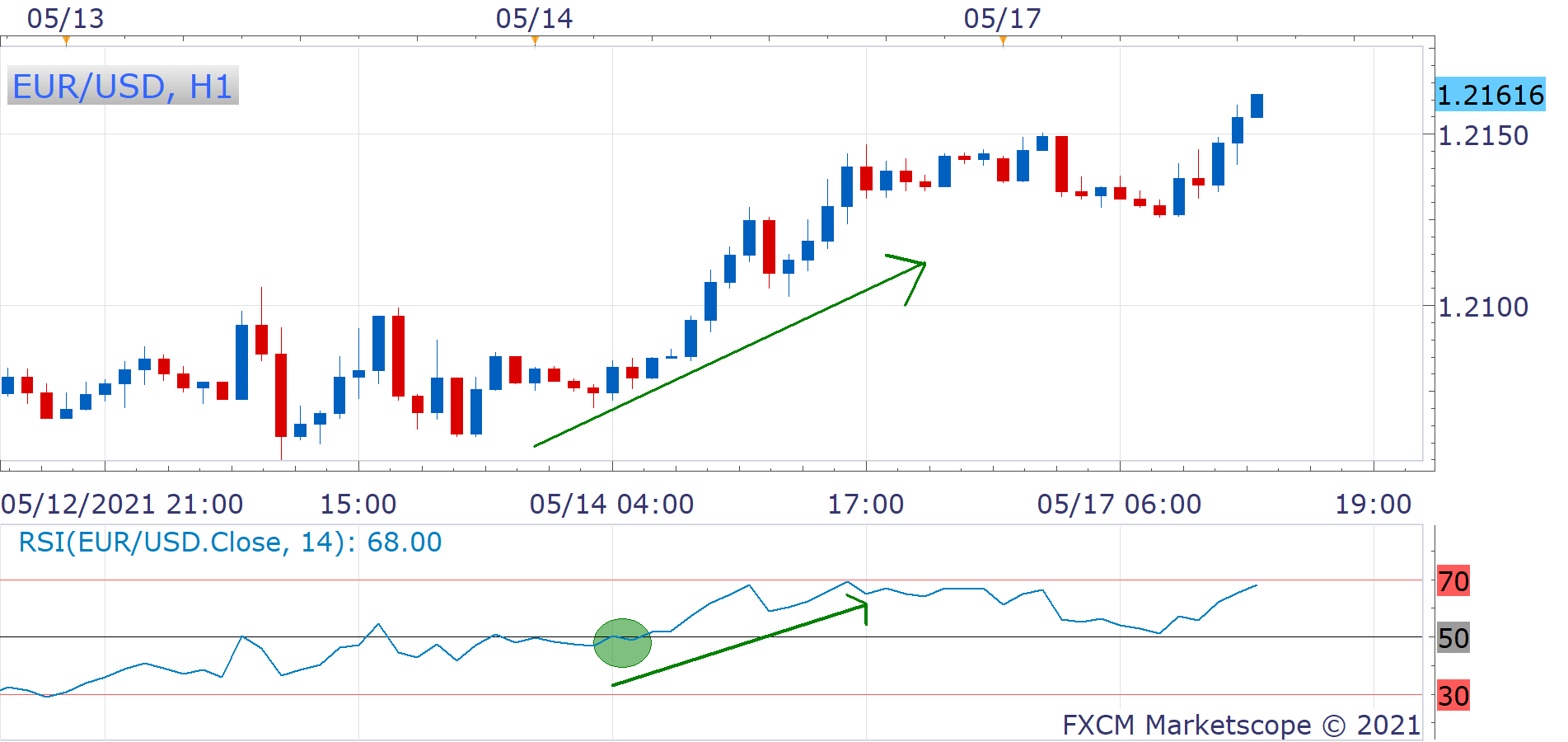
Swing Trading
Swing trading tends to be a medium-term forex trading strategy. It's often used over a period lasting between one day and one week. Swing traders will look to set up trades on 'swings' to highs and lows over a longer period of time. This is to filter out some of the 'noise', or erratic price movements that you can see in intraday trading.
These trading tactics can also help you avoid setting narrow stop losses that may force them to be 'stopped out' of a trade during a very short-term movement.
Pros
Swing trading forex strategies afford the trader with the chance to stay in the market – despite intraday volatility. This eliminates many unfortunate exits and can deliver a higher success rate than various short-term tactics. Not only that but profits from swing trades can be substantial. That is because you're more likely to get in on a trend by being active in the live market.
Cons
Executing swing trades is more expensive because stop losses are much greater in comparison to intraday forex strategies. Holding open positions for extended periods in the live market can also expose the trader to a higher degree of systemic risk. Meanwhile, there may be substantial costs attributable to forex rollover. This will be based on the pair and position size, however.
Example of Swing Trading
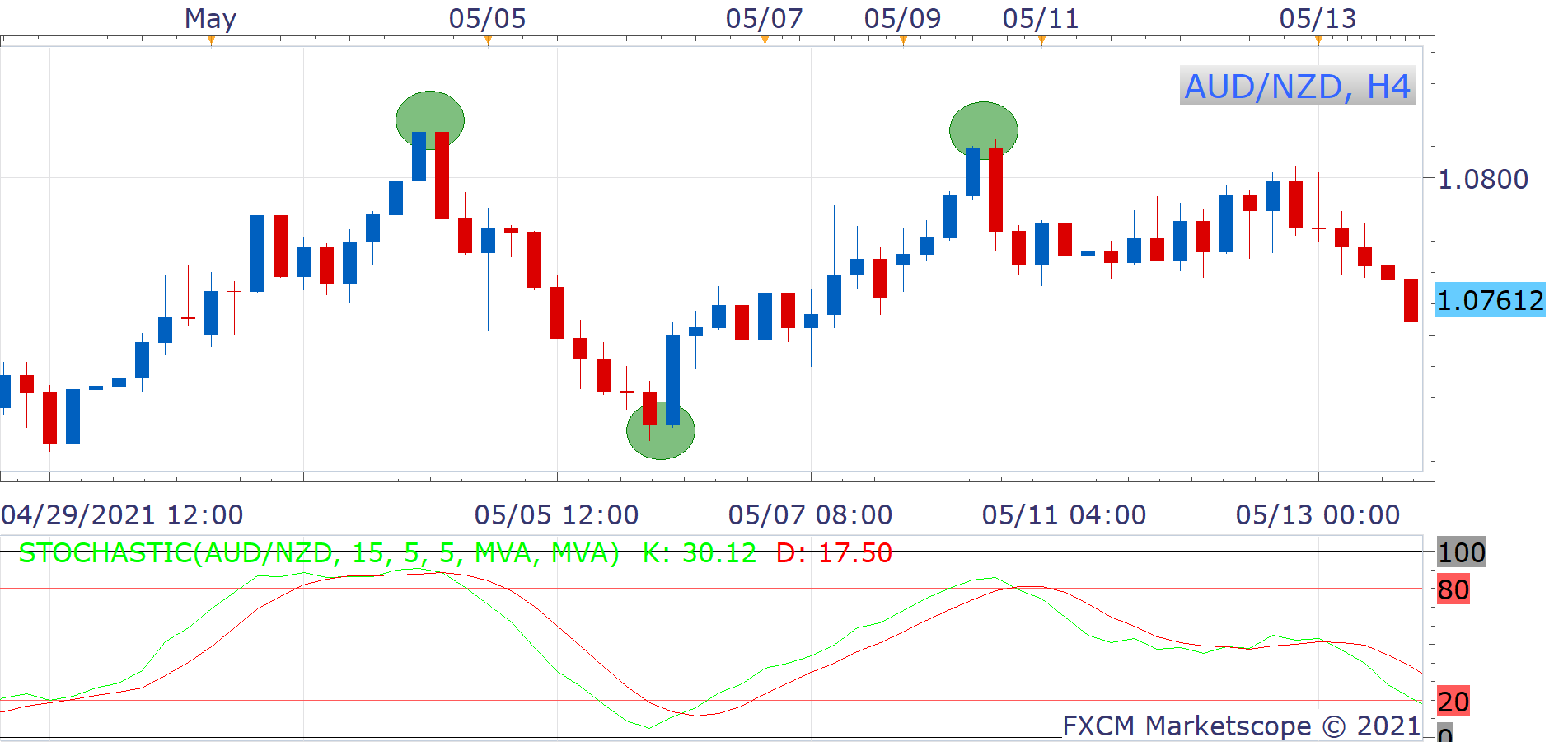
Breakout Trading
A breakout strategy is where traders try to spot an entry point at a breakout from a previously defined trading range. If the price breaks higher from the previously defined level of resistance on a chart, a trader may buy. This is based on the expectationthat the currency will continue to go higher. The opposite is also true if the price breaks a level of support.
The trader may then sell with the aim to buy once again at a more favourable price.
Pros
For some investors, breakouts create the best forex strategy because it can lead to big profits. The idea is that breakouts often turn into strong trends – and success rapidly becomes known. If there isn't ample order flow to support a directional move in price, the trader is able to exit the market and quickly mitigate losses.
Cons
While they do occur, true breakouts are not all too common on the forex market. Unfortunately, breakout traders frequently deal with false signals as market participation isn't strong enough to move price definitively. Breakouts can also be difficult to capture as they come on and develop extremely fast.
Example of Breakout Trading
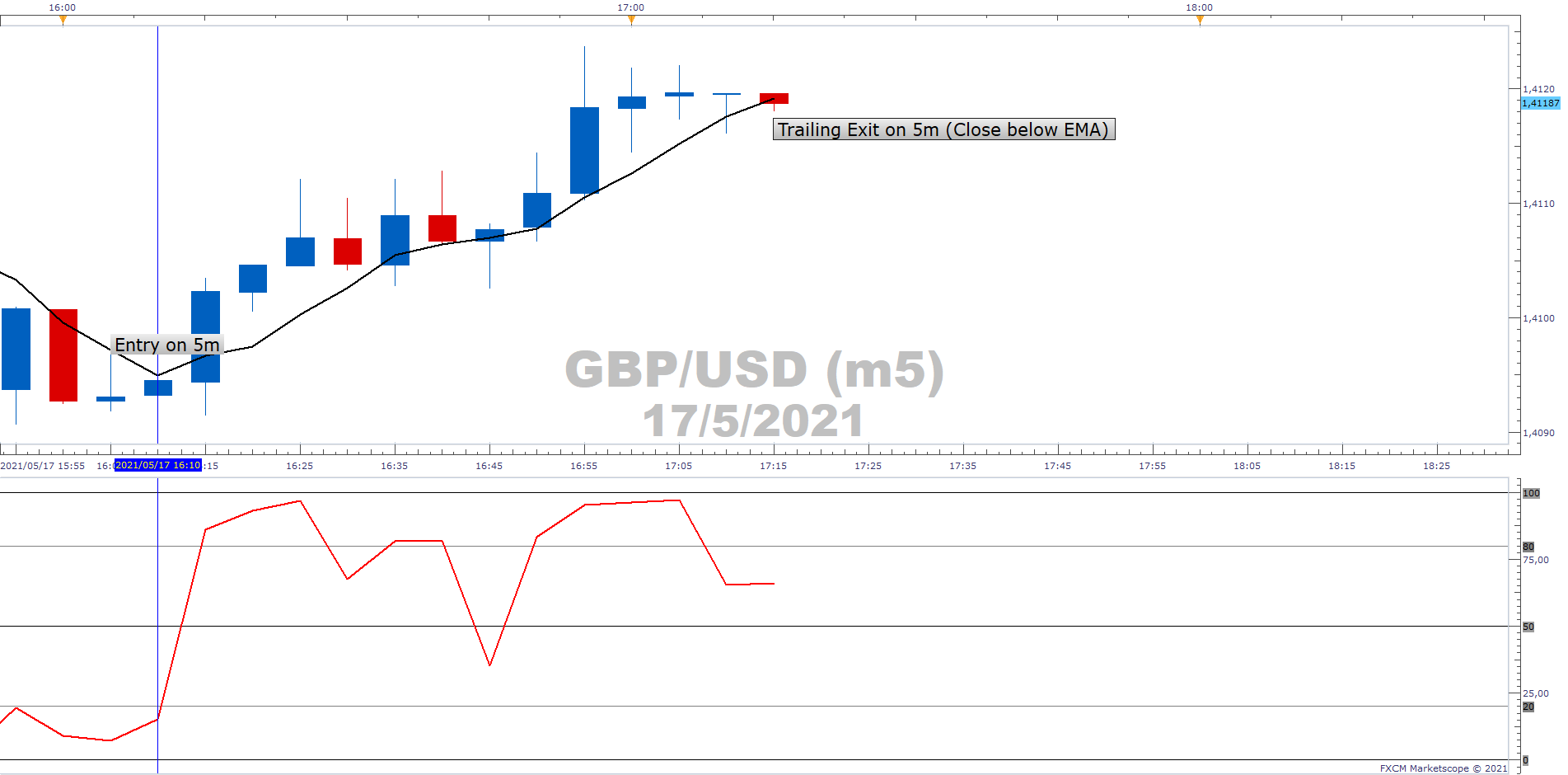
Forex Day Trading Strategy
By definition, day trading is when you open and close a position in any market in one session. It is sometimes seen in a negative light. But forex day trading strategies are legal and a valid way of engaging the capital markets. In fact, it benefits traders in several ways:
- Limited Risk: Forex day trading strategies are short-term. They don't require the trader to hold an open position in the market for an extended period. That means that exposure to systemic and market risks is greatly reduced.
- Decreased Opportunity Cost: A trading account's liquidity is ensured due to the intraday durations of trade execution. Risk capital is not committed to a single trade for a long period of time. As such, the trader is free to pursue other opportunities.
- Regular Cash Flow: Day trading strategies allow you to generate a regular flow of cash. Profits aren't guaranteed – but a daily P&L is calculated. As a result, gains are realised much faster compared to more traditional forex trading strategies.
A forex day trading strategy may be rooted in either technical or fundamental analysis. Some of the most common types will aim to capitalise upon breakouts, trending and range-bound pairs.
The availability of leverage and diverse options make forex a target-rich option for day traders compared to other markets. In addition, you can opt to go either long or short with a currency pair. When combined, these factors open the door to unique forex day trading strategies.
Pros
Day trading limits a trader's exposure to broader systemic risk. Also, there are no rollover costs because positions are not held through the daily forex close. Executing day trading strategies is more affordable as stop losses are vastly reduced from multi-day strategies.
In addition, opportunity cost is mitigated as capital is not tied up in the market for long periods.
Cons
When day trading, the trader is exposed to intraday noise. Breaking news items or scheduled economic reports can skew short-term volatility. As a result, it could cause unexpected losses. Slow market conditions can also undermine favourable risk vs reward ratios, which makes it a challenge to maintain your long-term profitability.
Example of Day Trading
Forex Scalping Strategy
Scalping is an intraday forex trading strategy that aims to take small profits on a frequent basis to produce a healthy bottom line. Trades are executed according to a rigid framework designed to preserve the integrity of an edge. Capital exposure and systemic risk are limited by applying a viable edge repeatedly on compressed timeframes.
The success of a forex scalping strategy depends on these key factors:
- Valid Edge: To make money by scalping, you must be able to identify positive expectation setups in the live market. This may be achieved in many ways, such as the use of algorithms, technical tools and fundamental strategies. A strong edge is statistically verifiable and potentially profitable.
- Discipline: Scalping requires the execution of a high volume of trades. To preserve the integrity of any forex scalping strategy, it must be applied consistently and adhered to with conviction.
- Low Costs: In scalping, profit targets are smaller than those of swing trades and long-term investment. Fees, commissions and spreads must be as low as possible to keep intact your bottom line.
- Strong Trade Execution: Successful scalping calls for precise execution. As such, orders must be placed and filled at market with maximum efficiency. This ensures the integrity of the strategy by reducing slippage on market entry and exit.
Due to a greater number of trades being executed, currency pairs that offer both liquidity and pricing volatility are ideal. This promotes efficient trade via tighter bid/ask spreads and limited slippage. As a result, this will increase the effectiveness of most scalping strategies.
Modern technology gives retail traders the ability to employ scalping methodologies remotely. Many brokers offer low-latency market access options and software platforms with advanced functionality. Whether or not your forex scalping strategy is fully automated, you will have a chance to use it in the marketplace.
Pros
As a forex trading technique, scalping strategies require you to use tight stop losses. This is essential to eliminate the chance of financial disaster. As trades are executed on compressed timeframes, exposure to systemic risk is vastly limited.
Not only that but risk capital is allocated for brief periods of time. This means that the trader can remain flexible in the market
Cons
Small profit targets and tight stop losses enhance the negative impacts of order slippage. The market liquidity must be robust, too. This is because wide bid/ask spreads and choppy price action can significantly undermine your strategy's success.
Scalpers rely on executing an abundance of trades on a daily basis. As such, it can often be challenging to find enough setups to sustain profitability.
Example of Scalping
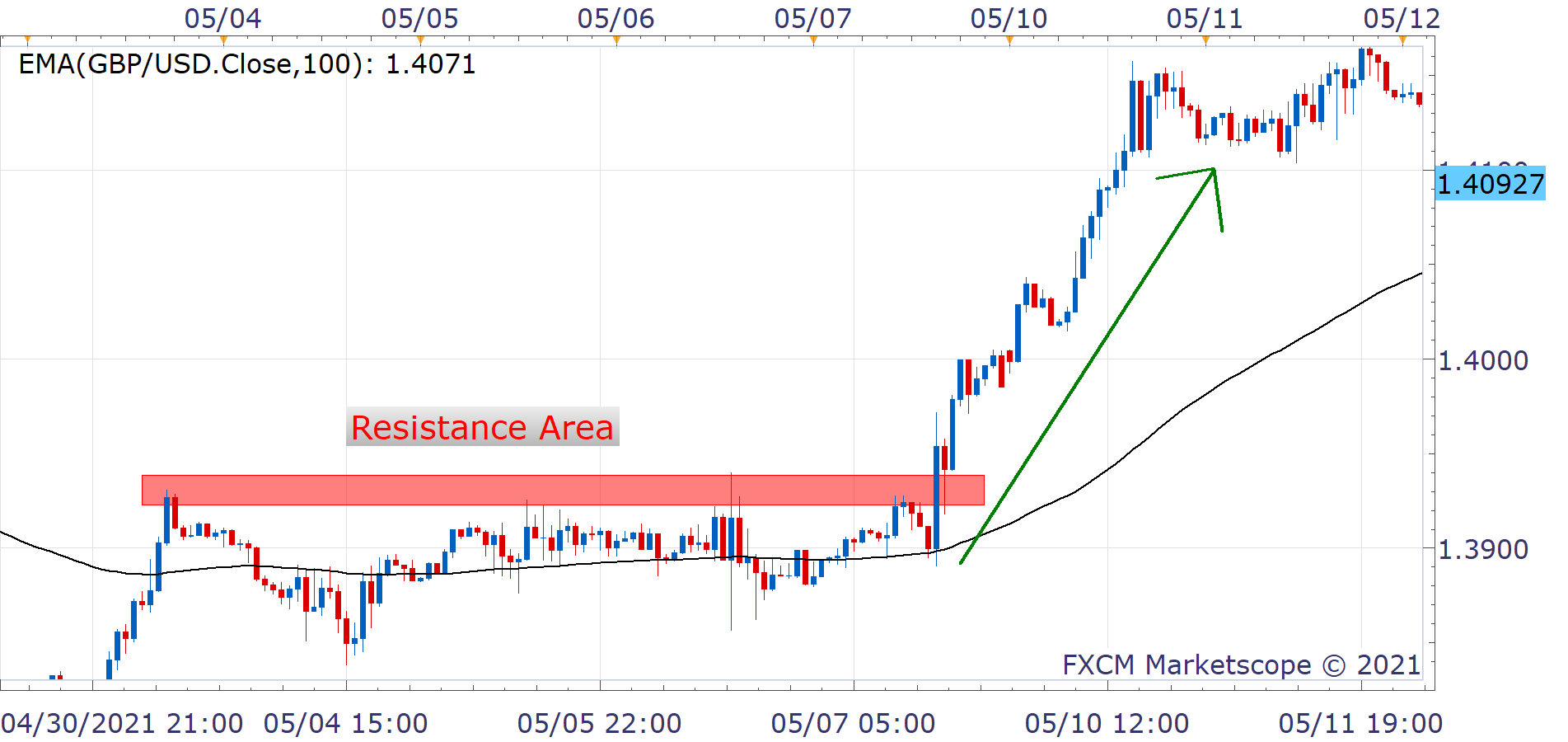
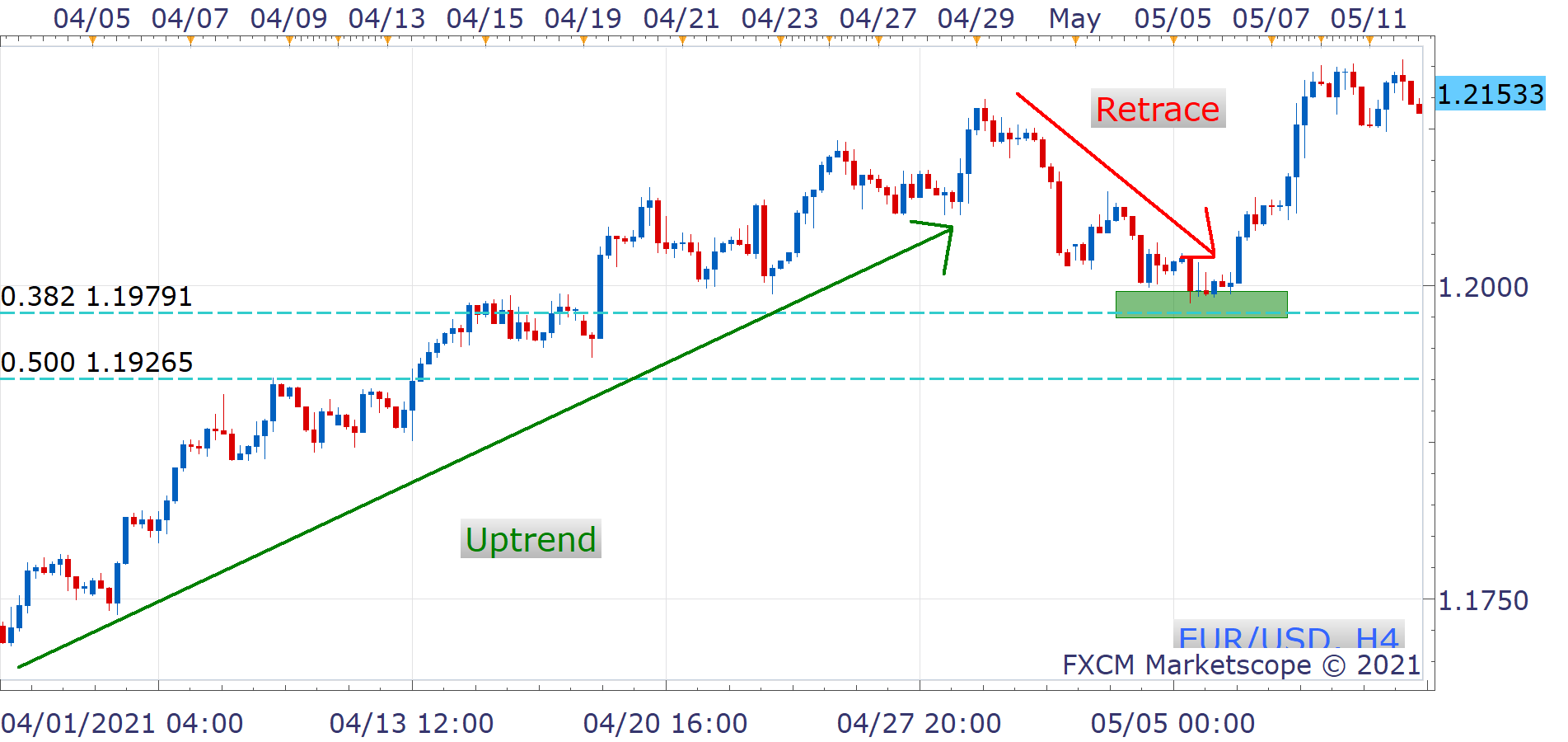
Retracement
Retracement strategies are based on the idea that prices never move in perfectly straight lines between highs and lows. Usually, a price will make some sort of a pause. It could also change direction in the middle of its larger paths between firm support and resistance levels.
With this in mind, retracement traders wait for a price to pull back – or 'retrace' – a portion of its movement. This is seen as confirmation of a trend before buying or selling in order for them to benefit from a longer and more probable price movement in one direction or another.
Traders often pick a particular percentage movement as a sign of confirmation (such as 50%). Fibonacci ratios (of 23.6%, 38.2% or 61.8%) can also be used. Either way, both help to identify optimal points for entering and exiting trades.
Pros
Buying or selling retracements is an ideal way of entering trending markets. It means that big profits are possible if you implement positive risk-vs-reward setups. You can also open positions in tandem with a prevailing trend, which typically leads to higher success rates than counter-trend forex trading strategies.
Cons
Trend reversals are often misconstrued as being retracements. If this happens, it can lead to substantial capital loss. A market frequently pulls back before going into a rotational phase – and this can effectively reduce a retracement trade's profit potential.
In trending markets, periodic ranges can be significant, so this requires a large capital outlay to properly use retracement trading strategies.
Example of Retracement
Reversal Trading
As the name implies, reversal trading is when traders seek to anticipate a reversal in a price trend. The aim is to guarantee an entry into a trade ahead of the market. This forex trading strategy is considered more difficult and riskier. True reversals can be difficult to spot but they're also more rewarding if they correctly predicted.
Traders use a range of tools to spot reversals, such as momentum and volume indicators. Visual cues on charts like triple tops and bottoms and head-and-shoulders patterns can also prove useful to reversal traders.
Pros
Reversal trading can lead to potential profits and the most ideal market entry for a new trend. There are numerous tools for identifying reversals – such as stochastics or the MACD. Stop losses can be affordable as a trade's effectiveness is determined in relation to the market's periodic extreme. From this point, a trend either will or won't change direction.
Cons
Spotting market reversals can be problematic as trending markets produce many false signals. In the live market, understanding the difference between a retracement and reversal is tough as the structure of both looks similar to start with. In addition, markets often lack ample follow through to fully change direction if a trend becomes exhausted.
Example of Reversal Trading
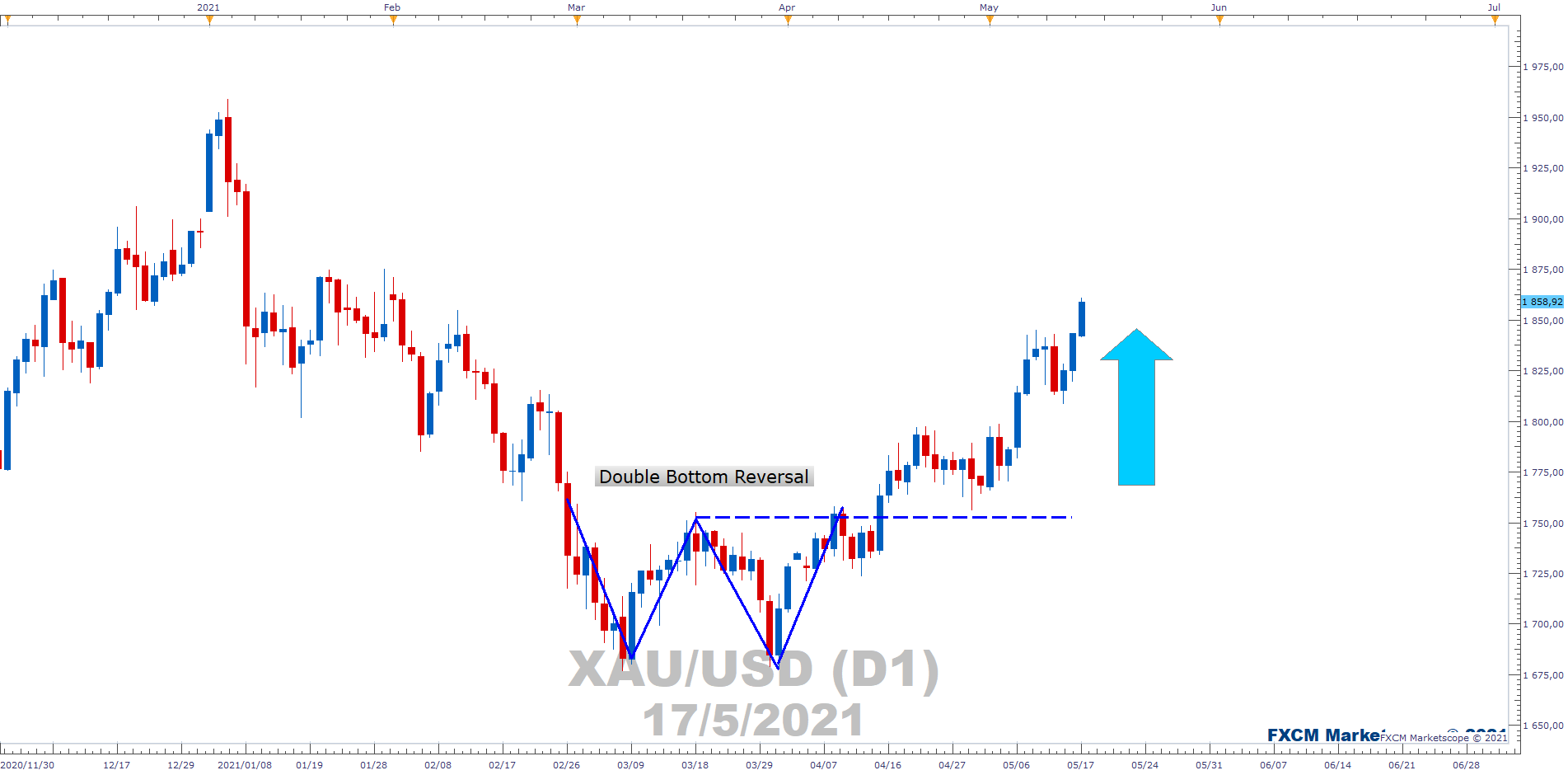
Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term forex strategy that may play out over periods of weeks, months or even years. Position traders often base strategies on the long-term macroeconomic trends of different economies. They also typically operate with low levels of leverage and smaller trade sizes with the expectation of possibly profiting on large price movements over a long period.
Such traders are more likely to rely on fundamental analysis together with technical indicators to choose their entry and exit levels. This type of trading may require greater levels of patience and stamina from traders, so it may not be desirable if you want to turn a fast profit.
Pros
Traders can potentially generate gains as they are in position to capitalise on strong trends. In addition, the trader is not concerned with short-term market volatility. Only the macro direction of the market matters when taking decisions. If position trading, you do not need to be precise in market entry or exit to maintain profitability.
Cons
Position trading strategies require you to hold open positions for extended periods. This ties up risk capital, directly increasing the opportunity cost. The exposure to systemic risk is also much greater than with shorter-term forex trading techniques. Losses can be large because stop loss locations are much wider in relation to macro market conditions.
Example of Position Trading
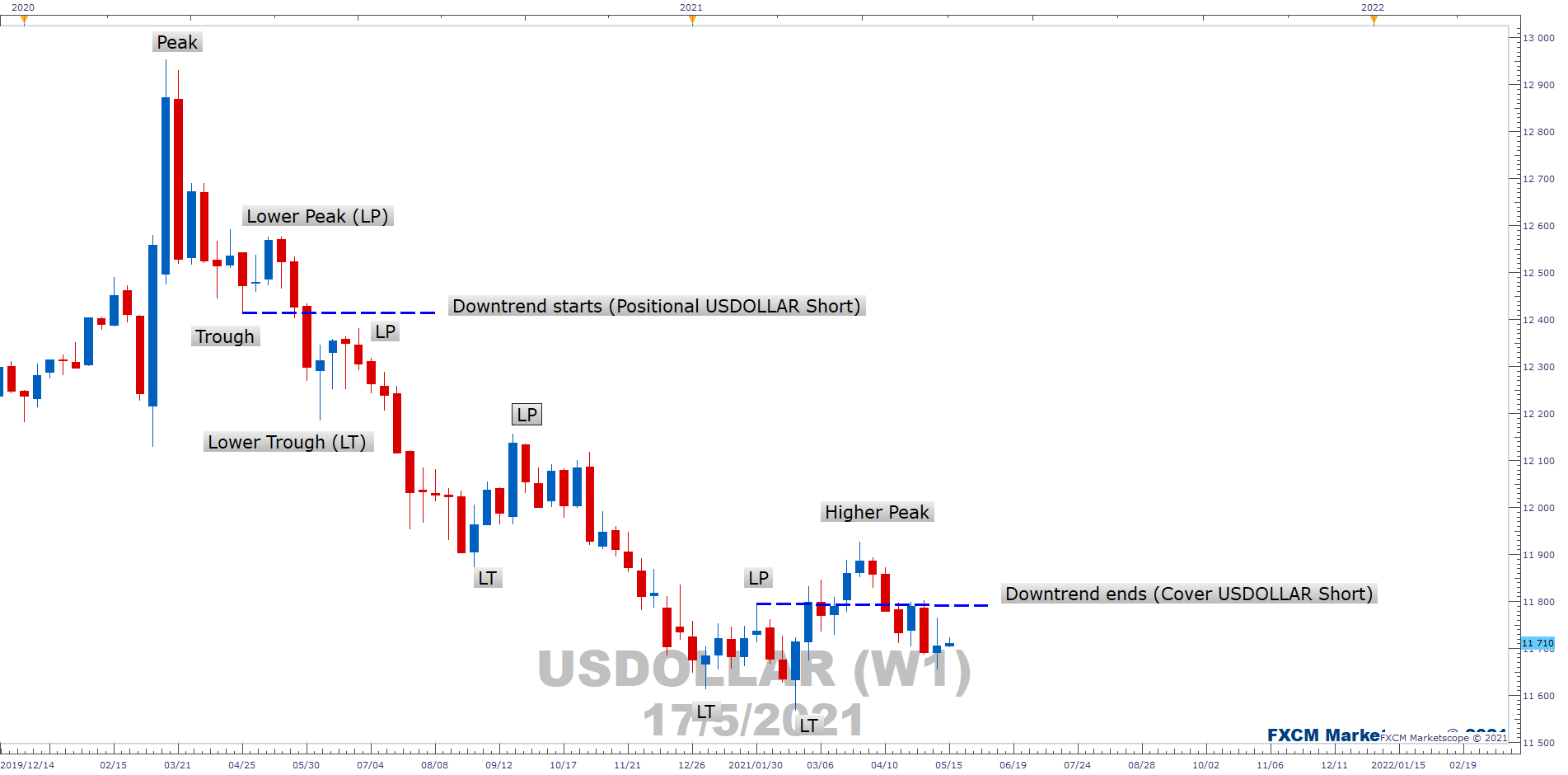
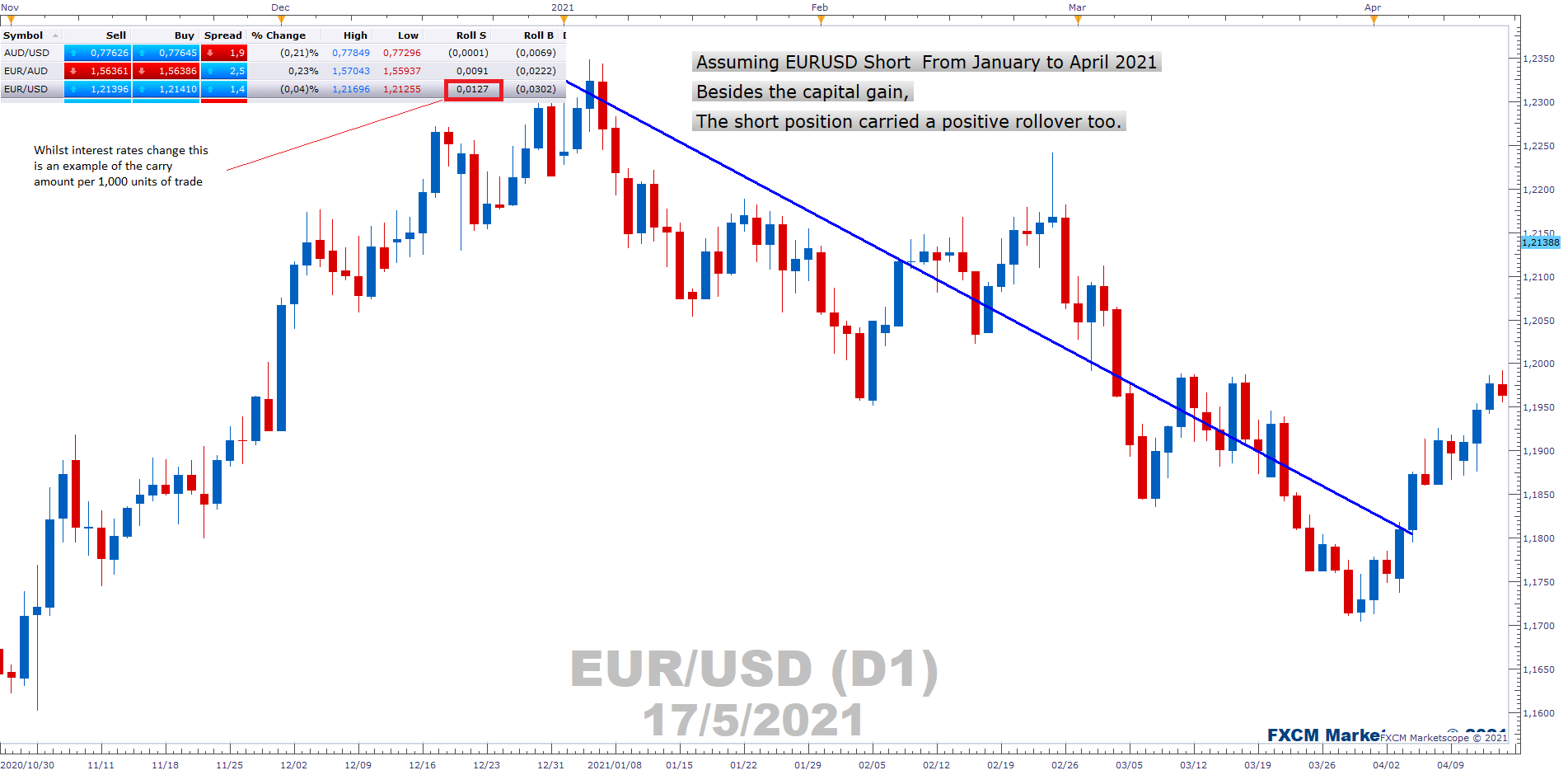
Carry Trade
Carry trade is a unique forex trading strategy. It seeks to enhance gains by taking advantage of the difference in interest rates between the countries of the currencies being traded.
Typically, traders holding currencies overnight are paid the interbank rate of the country of which the currency is bought. Carry traders, then, may seek a currency of a country with a low interest rate in order to buy one paying a higher rate – thus profiting from the difference.
Traders may combine trend and carry trading to ensure that any differences in currency prices – and interest earned – complement one another, rather than offsetting one another.
Pros
In a stable global economic environment, carry trades have a robust success rate. Carry trades are ideal for diversification because they may appreciate unlike separate stock or commodity positions. Carry trades are also straightforward and can produce regular cash flows.
Cons
The adoption of low interest rates by central banks can make the upside of certain carry trades negligible. This type of trading also has the added risk of being exposed to the economic situation in countries with 'higher' interest rates. If central bank policy suddenly shifts, a carry trade may be immediately compromised.
The same applies if an unfavourable economic report is published in – or about – that country.
Example of Carry Trading
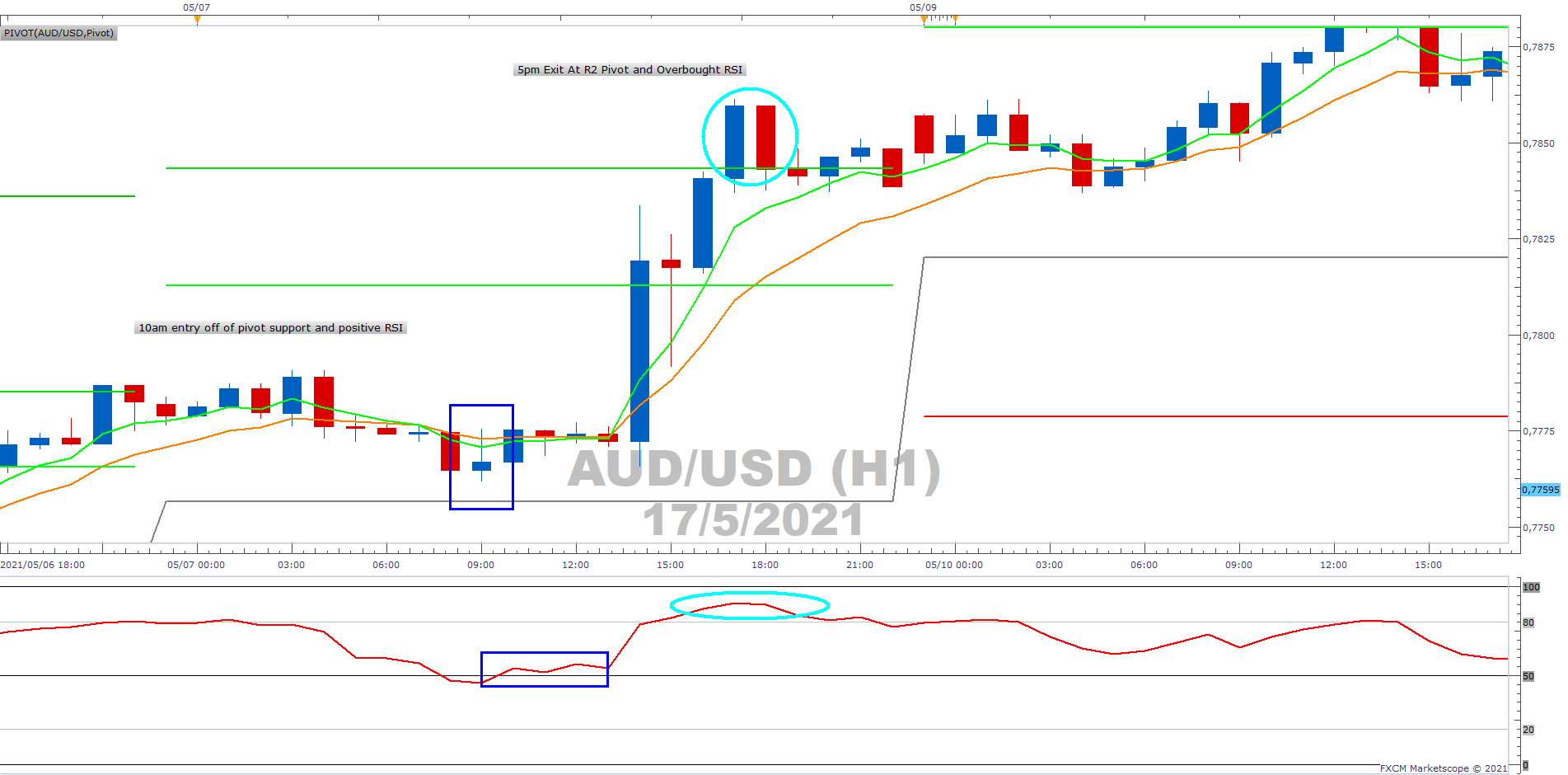
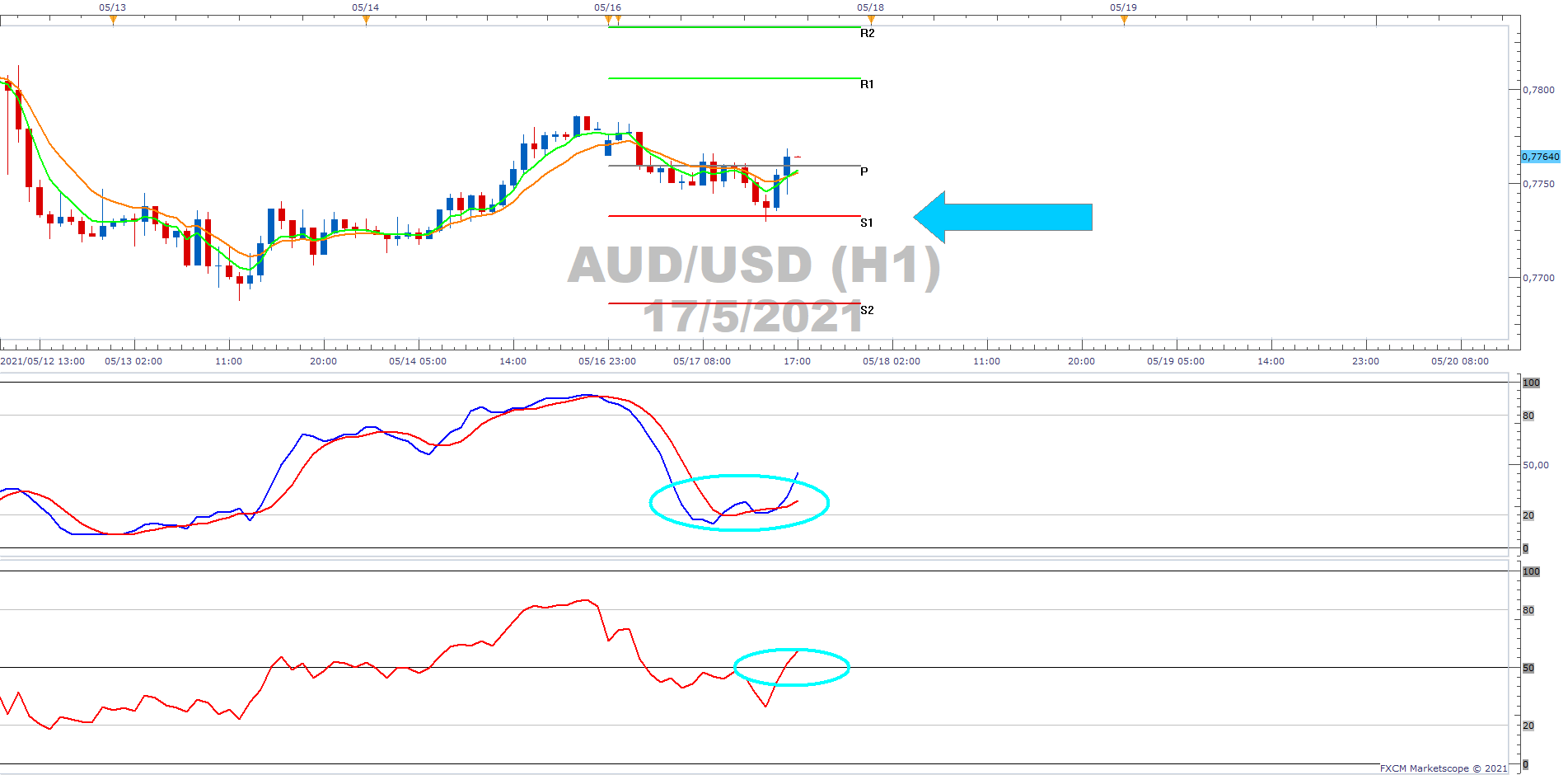
Pivot Points
Pivot point trading seeks to determine resistance and support levels based on an average of the previous session's high, low and closing prices. This average is used to help to predict the next likely highs and lows – as well as the intraday market reversals.
These averages are considered a healthy gauge for how long a short-term trend may continue because they are widely used in the market. They can also be used to see if a particular range was surpassed or if a new price trend breakout is occurring.
Pros
Pivot points give the trader viable support and resistance levels. They also help to identify any prevailing trends, reversals or breakout points. As such, pivots will take out a lot of the guesswork from market analysis. In addition, pivot points offer concrete market entry and exit points that you can incorporate into nearly any forex trading strategy.
Cons
In trending markets, pivot points can be unreliable. Surprise news events, economic releases or changes in fiscal policy can fast make their presence moot. Forex pricing may rarely reach either upper or lower pivot points when conditions are rotational or consolidating, too. If so, it makes the trading opportunities rare.
Example of Pivot Points
Contract-For-Difference (CFDs) Trading
A Contract-for-difference is a derivative product that lets you access the world's leading markets. CFDs are binding contracts between a trader and a broker. With a CFD, you agree to exchange the price difference of a product between when it is opened until it is closed.
CFDs allow you to profit from price movements of an underlying asset without actually owning it. Due to the fact that operations are conducted outside of standardised exchanges, CFDs are considered to be over-the-counter (OTC) products.
Here are some of the benefits of CFDs to active traders:
- Leverage: CFD products boost the purchasing power of traders, which makes it possible to open large positions with minimal capital. With available leverage at upwards of 30:1, these instruments feature limited margin requirements.
- Flexibility: Traders are free to take long or short positions in the market, so you're able to profit from rising or falling asset prices.
- Diversity: CFD listings are extensive and vary from broker to broker. Popular instruments are based upon corporate stocks, equity indices, currencies, commodities and debt products.
- Liquidity: A CFD is a contract with two parties: the trader and broker. This ensures liquidity because the broker is obliged to close any open positions held at market.
- Limited Costs: Costs are limited to the bid/ask spread. They are typically free from commissions – as well as maintenance fees.
There are also drawbacks to CFDs of which you should be aware, however:
- Enhanced leverage makes CFD trading inherently risky. Sudden spikes in volatility can greatly increase your exposure and lead to significant loss
- Bid/ask spreads can vary based on evolving market conditions and brokerage outlet. This can cut into profitability – but a comprehensive forex trading strategy can help you to manage these risks. As such, CFDs can become a practical way of trading the markets.
Fundamental Analysis
In fundamental analysis, traders look at the fundamental indicators of an economy to try to understand if a currency is undervalued or overvalued. The indicators can also show how its value is likely to move in relation to another currency.
Fundamental analysis can be highly complex. It involves many elements from a country's economic data that can indicate future trade and investment trends.
A good place for traders to start, however, is looking at currency inflows and outflows of an economy. These are often published and made available by the nation's central bank. Traders may rely on news and data releases from a country to get an idea of future trends.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is another of the forex trading strategies that is highly popular with traders. It often involves a review of the past and recent behaviour of currency price trends on charts to decide where they may move. The rationale for using technical analysis is that traders believe that market movements are ultimately dictated by supply, demand and mass market psychology.
As such, this establishes limits and ranges for currency prices to move upward and downward.
Technical analysis covers a long list of individual methods used to detect likely currency trends. Many traders appreciate technical analysis because they feel that it gives them an objective, visual and scientific basis for deciding when to buy and sell currencies.
What Is The Best Forex Trading Strategy For You?
The best forex strategy for any trader will come down to their knowledge, experience and risk appetite. What's right for one person is not necessarily right for the other so, when you are in the process of choosing a strategy, the first place to start is with yourself.
Be rigorous and honest in working out what forex trading strategies are suited to you. You can do this by completing a checklist that breaks down your trade-related assets. Consider your experience, your aims and the resources available to you.
Not doing this could make your trading experience more of a challenge than it needs to be.
The bottom line is that you need time, money and expertise to achieve your objective to generate a regular income from trading forex. You'll find that your best forex trading strategy is one that is aligns with and reflects where you are now - and where you want to be.
Put your forex strategy into practice with FXCM
Found the forex trading strategy that you think will work best for you? Put it into practice and trade the world's most popular currencies with FXCM today.
Our award-winning online trading platform gives you the chance to trade forex using CFDs or spread betting. And we are committed to providing all you need to help you achieve your trading goals.
To get started, simply open a live account with us today. You'll benefit from a broad range of currency pairs - as well as powerful trading platforms and round-the-clock support.
Are you new to trading and still not sure what forex trading systems you should use? Why not test out the various options about which you've read on this page with our demo account? It's a great way to access the markets without any of the risk.
Either way, make FXCM your platform of choice and enter the world of forex trading today.
This article was updated on 20th April 2021.
FXCM Research Team
FXCM Research Team consists of a number of FXCM's Market and Product Specialists.
Articles published by FXCM Research Team generally have numerous contributors and aim to provide general Educational and Informative content on Market News and Products.


Any opinions, news, research, analyses, prices, other information, or links to third-party sites contained on this website are provided on an "as-is" basis, as general market commentary and do not constitute investment advice. The market commentary has not been prepared in accordance with legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research, and it is therefore not subject to any prohibition on dealing ahead of dissemination. Although this commentary is not produced by an independent source, FXCM takes all sufficient steps to eliminate or prevent any conflicts of interests arising out of the production and dissemination of this communication. The employees of FXCM commit to acting in the clients' best interests and represent their views without misleading, deceiving, or otherwise impairing the clients' ability to make informed investment decisions. For more information about the FXCM's internal organizational and administrative arrangements for the prevention of conflicts, please refer to the Firms' Managing Conflicts Policy. Please ensure that you read and understand our Full Disclaimer and Liability provision concerning the foregoing Information, which can be accessed here.